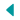
| Style | Commonwealth of Australia | United States of America |
| Type of Constitution | Federation of Sovereign States | Federation of Sovereign States |
| Type of Government | Constitutional Monarchy | Constitutional Presidential Republic |
| System of Government | Westminster Parliamentary System | Westminster Parliamentary System |
| Head of State | Monarch represented by Vice-Regal Governor-General | President |
| Head of Government | Prime Minister | President |
| Executive Power | Limited to Procedural & Ceremonial | Extensive Presidential Executive Powers |
| Upper House | Senate | Senate |
| Lower House | House of Representatives | House of Representatives |
| Highest Court | High Court of Australia | Supreme Court of the United States |
| Tenure of Justices | Must retire on attaining the age of 70 years | Lifetime |
| Franchise Administration | Australian Electoral Commission† with responsibility for Federal, State and Local Government elections (also industrial and commercial elections) and setting electoral boundaries | Various local & state jurisdictional methods |
| Suffrage | Universal and Automatic | Optional |
| Voting in all elections | Compulsory | Optional |
| Voting Process | Preferential ‡ | Simple Majority |
| Policing | Federal & State Police | Multiple Agencies at Federal, State & Local Government levels |
† Australian Electoral Commission
‡ Electoral Systems of Australian States and Territories